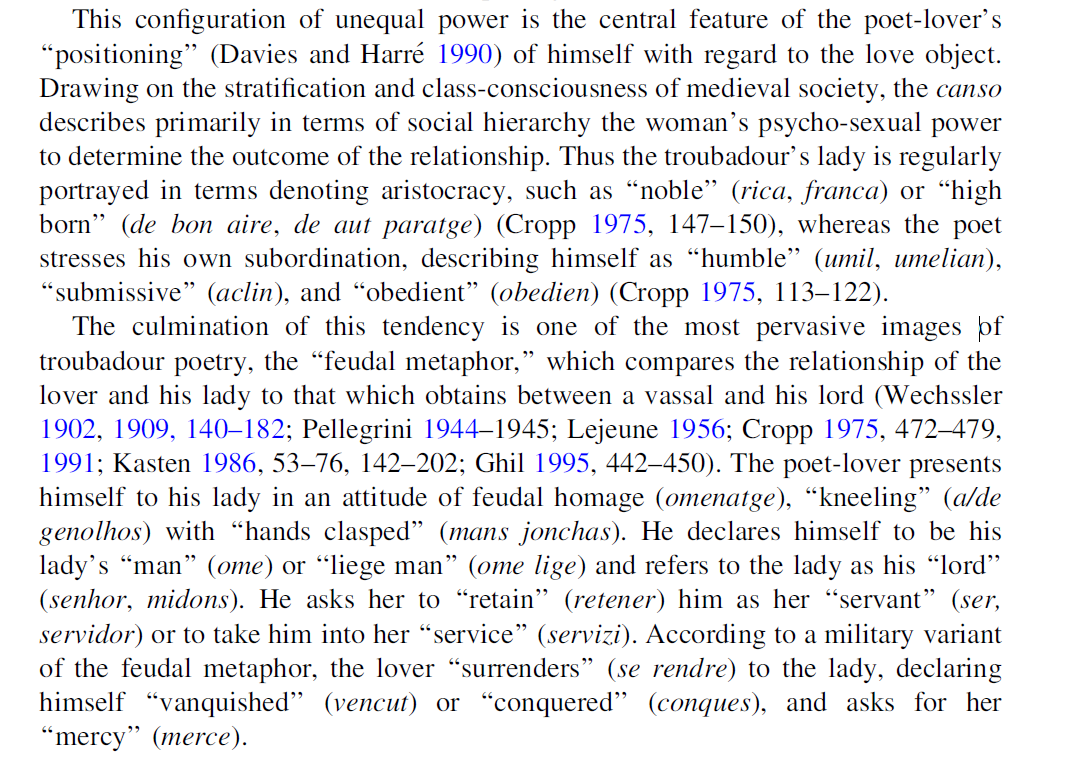
The following review of the concept gynocentrism is excerpted from A Clinical Guide to Discussing Prejudice Against Men, by Aman Siddiqi:
Gynocentrism
Gynocentrism refers to an exclusive or predominant focus on women or women’s interests (Wright, 2014; Wright & Elam, 2017). It is a form of positive prejudice towards women that results in negative consequences for men. Gynocentrism encourages male gender blindness by focusing attention and concern onto women, causing men and the issues they face to be overlooked or minimized. This, in turn, reinforces the gender disparity illusion. Since men’s issues are rarely discussed in the media or highlighted by organizations, the public assumes they do not exist. While addressing women’s issues is also meaningful, gynocentrism refers to the tendency for academia, the media, government and non-profit agencies to focus all, or nearly all, attention for gendered issues on women and girls.
First, issues that impact women occupy the majority of gendered discussions. They are discussed by the media and investigated by academics. The public is inundated with examples of issues women face. This disproportionate attention keeps the public unaware of men’s issues. In addition, instances of prejudice that are known by most people may be assumed to be of little importance because they are rarely discussed. Exclusionary attention to women’s issues also reveals that those in positions of authority do not deem instances of male suffering worthy of attention. This discourages the general public from paying those instances attention themselves. For example, ignorance of the issues men face has been suggested as one reason for the decline in male psychologists (Bottom et al., 2014).
Second, government agencies, academic research, and non-profit agencies dedicate the majority of their resources on gendered issues to women and girls. Numerous government and non-governmental agencies, such as the United Nations, World Bank, and International Monetary Fund, have divisions devoted to ending violence, improving health, encouraging education, and sponsoring entrepreneurship, exclusively for women. These agencies are replicated in countries around the world. In addition, innumerable non-profit organizations are either dedicated exclusively to women, or the gendered programs within larger organizations are dedicated to women.
The gynocentric view that only women deserve assistance is a consequence of the gender disparity illusion and the compassion void. Men’s suffering is either minimized, reframed to appear nongendered, or blamed on men themselves. The biased allocation of resources impacts the necessary services men and boys require, such as domestic violence shelters, health and wellness centers, educational programs and scholarships, and economic development programs. Similarly, academic research primarily focuses on gendered issues that women face. Dozens of journals are dedicated exclusively to women, and most gendered topic publications focus on women’s issues. Even publications in the journal Psychology of Men & Masculinity often focus on women, such as male sexual objectification of women (Mikorski &Szymanski, 2016) and male perpetrated dating violence (McDermott et al., 2017). Issues that men face are often ignored, even by those in the field of the psychology of men.
Third, gynocentrism results in the gendering of non-gendered issues. While some issues affect men or women disproportionately, many issues are non-gendered. In this case, there is no meaningful differentiation based on gender. However, an issue may be framed in a manner so it appears to disproportionately affect women. This serves to indirectly deny the equal suffering men experience by focusing all, or the majority, of resources and awareness on women’s experience of a non-gendered issue.
Gynocentrically gendering a nongendered issue may be facilitated by highlighting relevant statistics regarding only female victims. Even though the number of men and women impacted by an issue may be roughly the same, some publications only describe the impacts to women. This may cause the public to assume women are disproportionately impacted and deserve the majority of resources, even if it is not explicitly stated. The public may also assume men are not harmed by the issue simply because only the experiences of women are discussed. This is enabled by the male gender empathy gap. The suffering men experience through a non-gendered issue may be disregarded by researchers, so only the female victims are recognized.
An issue may also be gendered through gynocentric reframing. Women who experience a phenomenon may be described using positive terminology while men, impacted by the same issue, are described negatively. For example, female prisoners were referred to as “victims” of their environment, while male prisoners were called “violent” in the same article (Kearns, 2019). Attributions of malicious intentionality have been projected onto male perpetrators of domestic violence and sexual assault, while female perpetrators are described as being compelled by external forces into their actions (M. P. Johnson, 1995). This is an example of the ultimate attribution error, in which negative in-group (female) behaviors are attributed to external factors, but negative out-group (male) behaviors are attributed to personal characteristics (Pettigrew, 1979). This form of gynocentric reframing encourages the denial of victimhood, since causality for negative male behaviors is not linked to the social environment.
The dedication of public and private agencies to women, described in item two above, also encourages the gynocentric use of statistics. For example, the Department of Justice’s Office on Violence Against Women may feel justified in only publishing data regarding female victims of domestic violence and sexual assault since their mandate is to focus on women. This creates an “echo chamber” in which only statistics on women are published, leading people to believe an issue exclusively or predominately impacts women. This, in-turn, encourages resources and agencies be designed disproportionately for women, such as the Office on Violence Against Women.
Similarly, the United Nations’ Girls’ Education Initiative published a report detailing various barriers to girls’ education around the world (UNGEI, 2007). Items in the report include: poverty, social exclusion due to ethnicity, poor school conditions, overcrowded classrooms, and a lack of qualified teachers. The report claims that textbooks that promote gender stereotypes, inadequate water and sanitation, and violence near schools “are barriers that affect girls’ education in particular” (UNGEI, 2007, p. 3). However, these are all general barriers to education that impact boys and girls equally. The male gender empathy gap may cause the authors to disregard their impact on boys.
Fourth, gynocentric laws solidify institutional prejudice into society by creating differing requirements and protections for male and female citizens of the same country. For example, in the United States, the mandatory registration for selective service applies exclusively to men (Selective Service Registration, 2019). Furthermore, the male-only military draft is actively enforced in other countries around the world. As discussed further in the section entitled, “Examples of Prejudice Against Men,” numerous U.S. States, as well as foreign countries, specifically define rape as requiring a female victim. Laws, such as the Violence Against Women Act, provide government resources for women (Violence Against Women Act of 1994, 1994) and laws, such as the Female Genital Mutilation Act, define criminal actions as illegal only if the victim is female (Female Genital Mutilation Act, 1996). Similarly, the Indian penal code provides protection to wives that is not afforded to husbands (The Criminal Law (Second Amendment) Act 1983, 1983). This is only a sample of gendered laws that do not offer the same protection to, or enforce the same requirements on, all citizens equally.
Fifth, a gynocentric perspective may be used when interpreting gendered issues. When attributing meaning to events, evaluating the costs and benefits of gendered norms, or deciding who has control or agency in a situation, the perspectives of men are often overlooked or openly denied. While female perspectives are also meaningful, they may be taught in a manner which precludes any other views. A gynocentric bias has also been pushed onto descriptions of men’s own actions and desires. In this way, men’s own intentions, beliefs, and feelings are replaced with what others claim they intend, believe, and feel. This is an example of “speaking for men,” described in the section entitled, “Maintenance of the Acceptability of Prejudice Against Men.”
Similarly, a gynocentric perspective can bias the judicial system, resulting in unequal application of the law. For example, studies have shown men are given longer sentences for the same crime (Crew, 1991; Curry et al., 2004) and following a divorce, men are only made the custodial parent 17.5% of the time (Grall, 2016, p. 2013). The gynocentric perspective also impacts the mental health field. For example, Zander Keig is a transgender male who transitioned at age 39 (Bahrampour, 2018, Para. 15). Even though he is a clinical social worker, he admits that prior to his transition, he never considered men’s experiences or thoughts. He interpreted every case from a female perspective.
Sixth, a gynocentric viewpoint may give some women a feeling of superiority to men. They may begin to view themselves as deserving of preferential treatment. This can contribute to the belief in the transfer of hardship onto men. Psychological entitlement includes the belief that one deserves valuable possessions, praise, and is superior (W. K. Campbell et al., 2004). A study utilizing a nationally representative sample of 2,723 women and 1,698 men in New Zealand found that women’s endorsement of “benevolent sexism” was correlated (r = .41, p < .01) with psychological entitlement (Hammond et al., 2014). Described further in the section entitled “Maintenance of the Acceptability of Prejudice Against Men,” benevolent sexism is the term used to gynocentrically reframe prejudice in which men are compelled to serve women. Therefore, women who endorse the belief that men should provide them with preferential treatment were more likely to feel entitled. This was also described by Zander Keig, the transgender male mentioned above. He is in a position to compare his treatment by other women for the first 39 years of his life as a woman, to his treatment after transitioning to a male (Bahrampour, 2018). He states that now that he is a man, some women expect him to acquiesce and concede to them by letting them speak first, board a bus first, and let them sit down first. (Bahrampour, 2018).
Gynocentric social norms are still prevalent in modern society. For example, in some communities within the U.S., men are still expected to give up their seats to women, allow them to go before them in line, or provide other forms of preferential treatment. In some countries, this bias is solidified into law. For example, in India the front seating area on some public buses is reserved for women only, while the remaining are general seating. Men are forced to stand while seats are available because they are deemed unworthy of the right to rest. In addition, the general seating area is often occupied by female passengers, since the social norms upon which the regulation is based compel men to give up their seats to female passengers. Bus segregation was declared unconstitutional by the U.S. Supreme Court in 1956 and is considered a quintessential example of Jim Crow segregation (Browder v. Gayle, 1956). However, men face similar discrimination to this day. While not mandated by law in the U.S., these types of expectations still occur. For example, a video was recorded of a woman shouting and berating men on a subway train for not “being a gentleman” and giving her preferential treatment (Diinodiin Edits, 2019), and a similar incident was portrayed on an episode of Seinfeld (Cherones, 1992).
In contemporary society, gynocentrism has made romantic and sexual service to women expected of men. Some television, film, and academic publications teach or imply that it is men’s responsibility to provide romance and sexual satisfaction to a female partner. Men who do not provide romance to women may be portrayed as lazy and self-centered. For example, in an episode of The Big Bang Theory, the character Penny complains that her husband Leonard doesn’t “do anything for her anymore” and has “completely stop[ped] giving a crap” (Cendrowski, 2017). She states he “used to do all these things, like bring me flowers.” Later, she starts an argument with him and states, “since we got married you seem to think you don’t have to try anymore.” At this point, Leonard points out that he has provided all the romantic gestures in their relationship in the past, while she was mainly a recipient. In response, Penny decides to punish Leonard by canceling her vacation with him and taking her friend instead. This sends a message that not only are men obligated to provide romance to women, but if they point out the inequity of their situation, they should be punished.
Similarly, in an episode of Chuck, some characters become suspicious that a woman is cheating on her husband (Chandrasekhar, 2010). They confront the man and state, “I feel that if there is something wrong, it’s your fault.” The man then proceeds to list for them an average day in his life, in which he serves his wife, proving he is a good husband.
Most mornings, I wake up around 6. I pop a towel in the dryer so it’s warm when she gets out of the shower. I’ll whip her up a Belgian waffle or, you know, a goat-cheese omelet. Something easy. After Ellie’s foot rub, I’ll bike to the farmers’ market pick up fresh blueberries, or whatever’s in season. Come home, make her a smoothie. Organic nonfat milk, flaxseed oil. Something to give her a real midday kick-start. Once we’re in bed, post-lavender bath I spend about 20 minutes just watching her sleep.
He does all this while also being an emergency room physician. While the episode may be portraying an exaggerated view of the ideal husband, the premise is based on the overall assumption of romantic service to women. The episode sends the message that if a man does not serve his wife enough, she is justified in cheating on him.
Contemporary media also portrays men as owing sexual service to women. As an example of the agency bias, responsibility for a woman’s sexual enjoyment is attributed to her male partner, while his enjoyment is paid little attention and assumed to be his own responsibility. This expectation is demonstrated most clearly by the term “perform,” used to describe a man’s sexual relations with a woman. Men and women are not described as jointly participating in sexual relations. Instead, men are evaluated on their “performance,” defined by the degree to which they satisfy a female partner. The book She Comes First: The Thinking Man’s Guide to Pleasuring a Woman is a best-selling book that teaches men their job during sexis to satisfy women and provide them pleasure (Kerner, 2009). The author encourages men to derive their enjoyment from the act of serving their partner. He states, “What greater reward could a man ask for?” (Kerner, 2009, p. 20). A man experiencing pleasure himself is framed as selfish.
The author describes sexual intimacy as women receiving pleasure and men providing it. He goes as far as to justify the attack of Lorena Bobbitt against her husband by claiming that she cited his failure to sexually satisfy her as a reason. The gynocentric view of sexuality has become the norm for many in contemporary society. Men may be taught that they are selfish and unworthy unless they spend their sexual encounter focused exclusively on their female partner. On the other hand, women are taught that if they do not enjoy their experience or did not experience an orgasm, they should not look to their own absence of engagement. Instead, women should blame men for not serving them well enough. This was demonstrated by an Amazon reviewer who accused any man of not wanting to read, She Comes First: The Thinking Man’s Guide to Pleasuring a Woman as having too much “pride and ego” (Reviewer, 2018).
The gynocentric belief in male service to women has been enabled through the term chivalry. Historically, the term chivalry encompassed a variety of attributes such as bravery, loyalty, and generosity (Bax, 1913). However, over time chivalry was transformed into male service to women (Alfonsi, 1986). Men may also be shamed into service through accusations of not being a “gentleman;” therefore, equating being a gentleman with serving women. Prejudice against men is concealed by first reframing it as acts of chivalry, then attributing responsibility for the enforcement of chivalrous norms to men.
Positive Female Stereotypes
Gynocentrism also encourages the proliferation of positive female stereotypes. Positive prejudice is projected onto women through a gender-based halo effect. Women may be described as more empathetic, kinder, loving, elegant, honest, trustworthy, and peaceful than men. These stereotypes are used to deny instances of wrongdoing by women, at times shifting blame onto men. For example, domestic violence and sexual assault committed by women against men is often denied or trivialized, leaving male victims without help or recourse.
Studies have revealed that people hold a more positive view of women overall as compared to men. Attitude measures include variables such as how good vs. bad and valuable vs. useless men are compared to women (Eagly & Mladinic, 1994). Participants describe the percentage of each group they believe holds various characteristics, including their own views of how positive or negative those characteristics are. In addition, the affective responses that participants experience in response to men as compared to women are examined. Numerous studies have found that overall, participants hold more positive attitudes, stereotypes, and affective responses (i.e., feelings) towards women than men (Carter et al., 1991; Eagly et al., 1991; Eagly & Mladinic, 1989, 1994; Haddock & Zanna, 1994). This may be evidence of a global halo effect in which women are perceived as better people than men. This has been referred to as the “women are wonderful effect” (Eagly & Mladinic, 1994). This leads to implied negative stereotypes about men, resulting in bias and discrimination. For example, if people are unwilling to believe a woman is guilty of domestic violence, they may assume the victim is either lying or at fault themselves.
Positive prejudice may also be used to claim that women are superior to men in various ways. For example, Hillary Clinton stated that female leaders demonstrate more compassion and understanding than men because they lead “with the heart of a mother” (Zakaria, 2019). Similarly, President Obama explicitly stated that women are “indisputably” better leaders than men, and that the world would be a better place if only women were in leadership positions (Asher, 2019).
The belief in positive stereotypes about women can result in gynocentric projection, in which positive characteristics, or interpretations of actions, are projected onto women without evidence. This is demonstrated by entertainment media’s reluctance to portray evil female characters. Antagonist female characters are often provided a rationale to justify their behavior or are portrayed as a victim of circumstance. For example, in the film What Happened to Monday, the character named Monday is kidnapped in the beginning of the film (Wirkola, 2017). As the plot continues, each of her six sisters is targeted for murder one at a time by government agents. Eventually, the final two surviving sisters discover that Monday was not kidnapped, but in fact betrayed her sisters, allowing them to be murdered. However, instead of allowing a female character to be portrayed as evil or self-serving, the film provides her an excuse. The sisters discover that Monday was pregnant, and she chose to save her baby by having her six sisters murdered. This plot line demonstrates both the unwillingness of society to accept an evil female character, and purports that murdering six people is excusable since she is a mother.
Gynocentric projection is also demonstrated by researchers who project positive qualities onto women to explain negative behavior. For example, it has been alleged that female perpetrated domestic violence is motivated by a desire for “personal liberty” instead of controlling behavior, aggression, and impaired impulse control (Graham-Kevan, 2007b). Similarly, maternal filicide, mothers who kill their own babies, has been explained as either “altruistic,” for the betterment of the child, the result of psychosis, or unintentional (Friedman & Resnick, 2007). Any negative characteristics of the perpetrator herself are assumed to be absent. The only somewhat negative intentions suggested are the mother’s view of the baby as a hindrance, and the mother’s desire for revenge against the child’s father. However, these intentions can be justified respectively as a result of poverty, and the shifting of blame to alleged negative behaviors of the father.
As another example, a study was conducted to replicate Milgram’s famous study of obedience (Milgram, 1963). A sample of 13 men and 13 women were used to test their willingness to shock a puppy as a means of teaching it to solve problems (Sheridan & King, 1972). The voltage administered was increased with each successive incorrect solution. The participants were able to see the puppy’s reaction each time it was shocked. The problem was, in fact, unsolvable. The true purpose of the study was to see if the participants would continue shocking the puppy as the voltage and pain increased. Among the male participants, 7 of the 13 participants continued shocking the puppy until the completion of the experiment. The remaining 5 refused to continue at some point during the experiment. However, all 13 female participants shocked the puppy until the maximum setting.
The experimenters asked a separate set of 45 participants to estimate how men and women would behave in the above experiment. When female participants were asked how far the “average woman” would continue, 86% of female participants said an average woman would not go beyond one-third of the maximum level, and no participants stated the average woman would shock until the maximum. This demonstrates an overly positive belief that women would not cause harm to others. This belief was further demonstrated when this experiment was described in this author’s university’s introductory psychology class. Upon hearing that all the female subjects shocked the puppy to the maximum setting, the class was audibly shocked, confirming the same belief in positive prejudice towards women. Furthermore, the professor offered an explanation for the results, which denied any wrongdoing by the female participants. He told the class that the female participants “felt pressured by the experimenters to continue shocking the puppy,” so it was not really their fault. He implied they were forced into their actions, so the class could maintain their positive prejudice towards women. However, he offered no empirical data to support his explanation. Furthermore, the male subjects would have been equally pressured by the experimenters, yet they resisted. His irrational explanation demonstrates the lengths to which psychologists may go to maintain their positive beliefs towards women.
Terminology
Gynocentric terminology refers to gendered phrases which limit victimhood to women. The use of restrictive, exclusionary phrasing limits people’s empathy by referring to those in need of compassion and assistance as “women” instead of victims. For example, the major piece of U.S. legislation providing resources for domestic violence and sexual assault is named the Violence Against Women Act (U. S. Department of Justice, 2014). Similarly, the United Nations passed the “Protocol to Prevent, Suppress and Punish Trafficking in Persons, Especially Women and Children” (United Nations Human Rights, 2019). The document specifically highlights women as more important victims than men eight times in the document, such as to “combat trafficking in persons, especially women and children” (United Nations Human Rights, 2019, Para. 1).
An article was written in Minority Nurse about microaggressions in nursing against “nontraditional” students. Nontraditional was defined as “over the age of 25, ethnic minority groups, speaks English as a second language, a male, has dependent children, has a general equivalency diploma (GED), required to take remedial courses, and students who commute to the college campus [emphasis added]” (Doctor, 2018, Para. 1). Since 88.6% of nurses in the U.S. are female (U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2019a), men are a minority group. However, later in the article the author utilizes an exclusionary definition of microaggressions from the book Microaggressions in Everyday Life: Race, Gender, and Sexual Orientation. The author defines microaggressions as “verbal and nonverbal snubs, insults, putdowns, and condescending messages directed towards people of color, women, the LGBTQ population, people with disabilities, and any other marginalized group [emphasis added]” (Doctor, 2018, Para. 2). This definition specifically lists women as victims of microaggressions and excludes men; even though one of the subjects of the article on nursing is microaggressions against men. When readers and students are taught about microaggressions, they may be primed to assume men will never fall victim to them, or to disregard microaggressions men face as insignificant.
Avoiding gendered terminology has been a major goal of gender studies for decades. For example, the term mankind is replaced with humankind or peoplekind, Time magazine’s “Man of the Year” award was changed to “Person of the Year,” and Cornell’s Society of Hotelmen was changed to the Cornell Hotel Society. Guidelines from the American Psychological Association now encourage the use of a singular form of “they” and “their” in place of “he or she” and “his or hers” (American Psychological Association, 2019). When gendered terminology contributes to excluding women, society makes a point to change it. However, when gendered terminology excludes men, it is often maintained or justified.
For example, at a town hall meeting with Prime Minister Justin Trudeau, an individual raised a question about difficulties young people face who desire to volunteer through a charitable religious organization in Canada (The Trudeau Follies, 2018). At the end of her question she stated, “We cannot do free volunteering to help our neighbors in need as we truly desire. So, that’s why we came here today to ask you, to also look into the policies that religious charitable organizations have in our legislation so that it can also be changed, because maternal love is the love that’s going to change the future of mankind. So we’d like you to…” At this point Prime Minister Trudeau interrupted her and said, “We like to say peoplekind, not necessarily mankind;” which was followed by applause. The Prime Minister’s interest in gendered terminology is so strong, his first point when addressing her question about charitable volunteering was to point out her use of the term “mankind.” However, the questioner also stated that “maternal love” is the most important force for change. The use of this gendered phrase went undiscussed. This demonstrates a bias in which gendered terminology that positively impacts women is maintained.
Gynocentric terminology is also used to deny the existence of male victims of domestic violence and sexual assault, excluding them from recognition and services. Victims may be referred to as “women” and perpetrators as “men.” This is often justified by claiming that the majority of those affected are female. However, this argument is based on two fallacies. First, the assumption that women are disproportionately impacted by these crimes is empirically false, described in the section entitled “Examples of Prejudice Against Men.” Second, and more importantly, the percentage of men and women who suffer from these crimes is irrelevant. All victims deserve concern and respect. Even if an individual believes more women are impacted, male victims should never be erased or overlooked. As described above, modern social standards have already determined that excluding a gender through exclusionary terminology is discriminatory. For example, even though 85% of the military is male (Coleman, 2014), and
97.6% of fatalities of active duty U.S. military personnel and Reservists in the Afghanistan and Iraq wars have been male (DeBruyne, 2019), we always use the term “men and women in the military.” Erasing male victims of domestic violence and sexual assault can never be justified by one’s belief that more women are impacted than men. Every individual knows that 100% of victims are not female. Persistence on using the term “women” in place of victims is a statement that male victims do not deserve recognition. This form of gynocentric terminology most clearly demonstrates how an overemphasis on women and women’s issues becomes a form of prejudice against men.
References
American Psychological Association. (2019). Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (Seventh edition). American Psychological Association.
Asher, S. (2019, December 16). Obama: Women are better leaders than men. BBC News. https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-50805822
Alfonsi, S. R. (1986). Masculine submission in troubadour lyric (Vol. 34). Peter Lang Publications.
Bahrampour, T. (2018, July 20). Crossing the divide. Do men really have it easier? These transgender guys found the trugh was more complex. The Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/local/wp/2018/07/20/feature/crossing-the-divide-do-men-really-have-it-easier-these-transgender-guys-found-the-truth-was-more-complex/?utm_term=.0b551274996f
Bax, E. B. (1913). The fraud of feminism. Grant Richards.
Bottom, T. L., Gouws, D., & Groth, M. (2014). The Influence of academia on men and our understanding of them. New Male Studies, 3(2), 69–92.
Browder v. Gayle, 352 U.S. 903 (1956).
Campbell, W. K., Bonacci, A. M., Shelton, J., Exline, J. J., & Bushman, B. J. (2004). Psychological entitlement: Interpersonal consequences and validation of a self-report measure. Journal of Personality Assessment, 83(1), 29–45. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327752jpa8301_04
Carter, J., Lane, C., & Kite, M. (1991). Which sex is more likable? It depends on the subtype. Meeting of the American Psychological Society, Washington, DC.
Cendrowski, M. (2017, January 19). The romance recalibration (10:13). In The Big Bang Theory. Warner Bros. https://www.imdb.com/title/tt6337212/?ref_=ttep_ep14
Cherones, T. (1992, January 8). The Subway (3:!3). In Seinfeld. Castle Rock Entertainment.
Coleman, D. (2014, July 24). U.S. military personnel 1954-2014: The numbers. History in Pieces. https://historyinpieces.com/research/us-military-personnel-1954-2014
Crew, B. K. (1991). Sex differences in criminal sentencing: Chivalry or patriarchy? Justice Quarterly, 8(1), 59–83. https://doi.org/10.1080/07418829100090911
Curry, T. R., Lee, G., & Rodriguez, S. F. (2004). Does victim gender increase sentence severity? Further explorations of gender dynamics and sentencing outcomes. Crime &Delinquency, 50(3). https://doi.org/10.1177/0011128703256265
DeBruyne, N. F. (2019). American war and military operations casualties: Lists and statistics. Congressional Research Service.
Diinodiin Edits. (2019, February 14). Why are you not being a gentleman (Original) [Video file]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t4VhoyN6jpE
Doctor, A. (2018, July 20). Microaggressions in the nursing classroom environment. Minority Nurse. https://minoritynurse.com/category/bullying-in-nursing/
Eagly, A. H., Mladinic, A., & Otto, S. (1991). Are women evaluated more favorably than men?: An analysis of attitudes, beliefs, and emotions. Psychology of Women Quarterly, 15(2), 203–216. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-6402.1991.tb00792.x
Eagly, A. H., & Mladinic, A. (1989). Gender stereotypes and attitudes toward women and men. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 15(4), 543–558.https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167289154008
Eagly, A. H., & Mladinic, A. (1994). Are people prejudiced against women? Some answers from research on attitudes, gender stereotypes, and judgments of competence. European Review of Social Psychology, 5(1), 1–35. https://doi.org/10.1080/14792779543000002
Female Genital Mutilation Act, 18 U.S.C. § 116 (1996).
Friedman, S. H., & Resnick, P. J. (2007). Child murder by mothers: Patterns and prevention. World Psychiatry, 6(3), 137–141.
Graham-Kevan, N. (2007b). Domestic violence: Research and implications for batterer programmes in Europe. European Journal on Criminal Policy and Research, 13(3), 213– 225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10610-007-9045-4
Grall, T. (2016). Custodial mothers and fathers and their child support: 2013 (No. P60-255). U.S. Census Bureau. https://www.census.gov/library/publications/2016/demo/p60-255.html
Haddock, G., & Zanna, M. P. (1994). Preferring “Housewives” To “Feminists”: Categorization and the Favorability of Attitudes Toward Women. Psychology of Women Quarterly, 18(1), 25–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-6402.1994.tb00295.x
Hammond, M. D., Sibley, C. G., & Overall, N. C. (2014). The allure of sexism: Psychological entitlement fosters women’s endorsement of benevolent sexism over time. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 5(4), 422–429.https://doi.org/10.1177/1948550613506124
Johnson, M. P. (1995). Patriarchal terrorism and common couple violence: Two forms of violence against women. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 57(2), 283–294. https://doi.org/10.2307/353683
Kearns, M. (2019, October 10). Elizabeth Warren throws women under the bus in the name of LGBTQ rights. National Review. https://www.nationalreview.com/corner/elizabeth-warren-throws-women-under-the-bus-in-the-name-of-lgbtq-rights/
Kerner, I. (2009). She comes first: The thinking man’s guide to pleasuring a woman (Reprint edition). HarperCollins e-books.
McDermott, R. C., Naylor, P. D., McKelvey, D., & Kantra, L. (2017). College men’s and women’s masculine gender role strain and dating violence acceptance attitudes: Testing sex as a moderator. Psychology of Men & Masculinity, 18(2), 99–111. https://doi.org/10.1037/men0000044
Mikorski, R., & Szymanski, D. M. (2016). Masculine norms, peer group, pornography, Facebook, and men’s sexual objectification of women. Psychology of Men & Masculinity, 18(4). https://doi.org/10.1037/e516842016-001
Milgram, S. (1963). Behavioral study of obedience. The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 67(4), 371–378. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0040525
Pettigrew, T. F. (1979). The ultimate attribution error: Extending Allport’s cognitive analysis of prejudice. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 5(4), 461–476. https://doi.org/10.1177/014616727900500407
Reviewer. (2018, December 26). I learned things about my body from a man?! Amazon. https://www.amazon.com/gp/customer-reviews/R3AITSKW9J2IZ7/ref=cm_cr_dp_d_rvw_ttl?ie=UTF8&ASIN=B000FC1PRK
Sheridan, C. L., & King, R. G. (1972). Obedience to authority with an authentic victim. Proceedings of the Annual Convention of the American Psychological Association, 7,165–166. https://doi.org/10.1037/e465522008-083
The Criminal Law (Second Amendment) Act 1983, 1860 Indian Penal Code § 498A (1983). http://www.ilo.org/dyn/natlex/natlex4.detail?p_lang=en&p_isn=93631
The Trudeau Follies. (2018, February 3). It’s Peoplekind… Not mankind says Trudeau [Video file]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cR9MuNnznFU&feature=emb_logo
UNGEI. (2007). United Nations girls’ education initiative. United Nations.
United Nations Human Rights. (2019). Protocol to prevent, suppress and punish trafficking in persons, especially women and children. United Nations Convention Against Transnational Organized Crime. https://www.ohchr.org/EN/ProfessionalInterest/Pages/ProtocolTraffickingInPersons.aspx
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. (2019a). Labor force statistics from teh current population survey. U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. https://www.bls.gov/cps/cpsaat11.htm
Violence Against Women Act of 1994, 34 U.S.C. § 12291-12512 (1994).
Wirkola, T. (2017, August 18). What Happened to Monday [Action, Crime, Drama, Mystery, Sci-Fi, Thriller]. Vendome Pictures, Nexus Factory, Raffaella Productions.
Wright, P. (2014). Gynocentrism: From feudalism to the modern Disney princess. Amazon Digital.
Wright, P., & Elam, P. (2017). Red pill psychology: Psychology for men in a gynocentric world. Amazon Digital.
Zakaria, F. (2019, April). Hillary Clinton on how women lead differently. CNN. https://edition.cnn.com/videos/tv/2019/04/12/exp-gps-0414-hillary-clinton-on-women-leadership.cnn
*The above excerpt republished with permission of the author.
* * *